Have you ever heard of the term “digital twin”? It’s a concept that has been gaining a lot of attention in recent years, especially in the realm of technology and innovation. In this blog post, we will explore what a digital twin is, how it works, and its potential applications in various industries.
What is a Digital Twin?
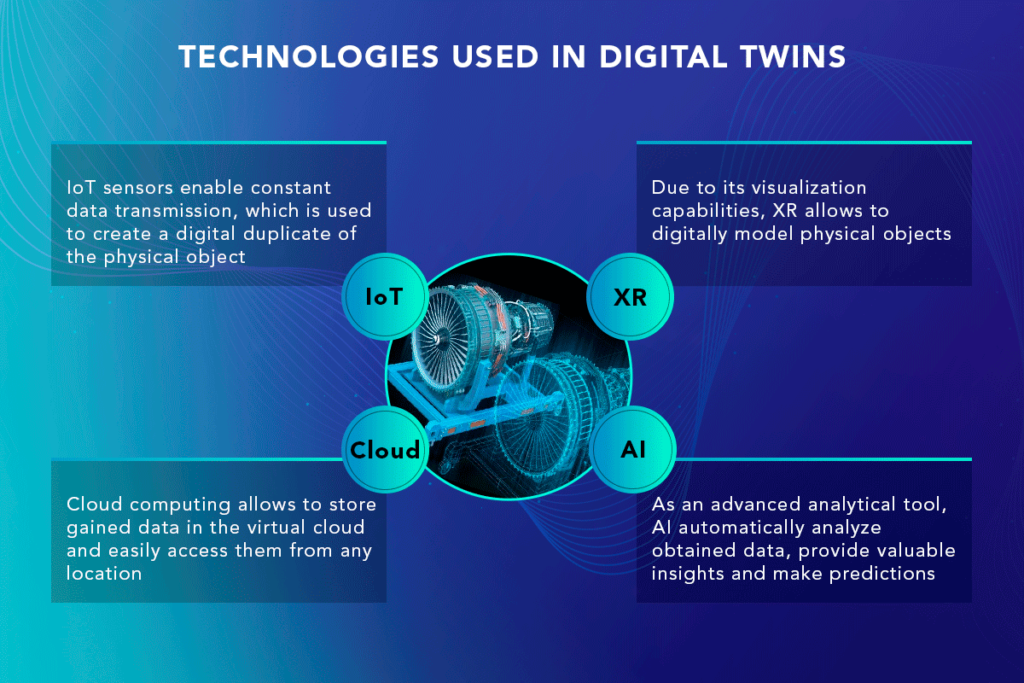
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object, process, or system. It is created by collecting real-time data from sensors, devices, and other sources and using advanced analytics and algorithms to create a digital replica. This digital twin can then be used to monitor, simulate, and optimize the performance of the physical object or system.
Think of a digital twin as a mirror image of its physical counterpart, capturing all the relevant information and characteristics that make it unique. It provides a real-time view of the physical object’s behavior, allowing for better understanding, analysis, and decision-making.
How Does a Digital Twin Work?
The process of creating a digital twin involves several steps. First, data is collected from various sources, such as sensors, IoT devices, and historical records. This data is then processed and analyzed using machine learning algorithms to identify patterns, correlations, and anomalies.
Once the digital twin is created, it can be used for a variety of purposes. For example, it can be used to monitor the performance of a machine in a factory, predict maintenance needs, and optimize its operation. It can also be used to simulate different scenarios and predict the impact of changes or improvements.
Furthermore, a digital twin can be used to improve the design and development process. By creating a virtual model of a product or system, engineers and designers can test different configurations, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions before the physical prototype is built.
Applications of Digital Twin
The concept of digital twin has a wide range of applications across different industries. Here are a few examples:
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, digital twins can be used to monitor and optimize the performance of machines, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency. By analyzing real-time data from sensors, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, reduce downtime, and increase productivity.
Healthcare
In healthcare, digital twins can be used to create personalized treatment plans, simulate surgical procedures, and monitor patient health. By combining data from wearables, medical devices, and electronic health records, healthcare providers can make more accurate diagnoses and provide better care.
Smart Cities
In the context of smart cities, digital twins can be used to monitor and manage infrastructure, such as buildings, roads, and utilities. By analyzing real-time data, city planners can identify areas for improvement, optimize resource allocation, and enhance the overall livability of the city.
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, digital twins can be used to monitor the performance of aircraft, predict maintenance needs, and optimize fuel consumption. By analyzing data from sensors and flight records, airlines can reduce costs, improve safety, and enhance the passenger experience.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, the concept of digital twin holds great promise for a wide range of industries. By creating virtual replicas of physical objects and systems, organizations can gain valuable insights, optimize performance, and make informed decisions. Whether it’s in manufacturing, healthcare, smart cities, or aerospace, digital twins have the potential to revolutionize the way we design, monitor, and interact with the world around us.
